RESOURCES
Training Material
This Tutorial Video is a recording of an EMB3Rs workshop. It is made to guide users through the application of the heat and cold matching platform.
Introduction
00:00 – Presentation of the EMB3RS project and platform
Instructions for building simulation on the EMB3RS platform
30:12 Creating sources on the EMB3RS platform
39:06 Creating sinks on the EMB3RS platform
54:06 Creating the simulation on the EMB3RS platform
1:06:00 Running the simulation on the EMB3RS platform
Ending
1:07:58 – Explanation of the reports
D6.8 – Training Materials
GUIDEBOOK
This report presents the training materials for the EMB3RS platform. These materials aim at guiding users on how to work with the platform and illustrating different platform functionalities. In particular, this report includes step by step instructions with illustrations to run 3 different simulation types, using a demo case in the EMB3RS platform. The demo case consists of 4 industrial sources of excess heat and also includes a total of 8 sinks, consisting of 5 industrial sinks, the district heating and cooling systems in a nearby town, a greenhouse and a building. The different types of sinks are used to demonstrate different types of characterisations that can be performed in the platform. Three different types of simulations are performed: the full simulation i.e., simulation calling all modules, and 2 internal heat recovery simulations, i.e., Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) and pinch analysis.
These training materials have been used in 1 internal workshop and 2 external stakeholder workshops where participants were able to successfully run simulations using these materials. The feedback received in the context of such workshops has helped to improve and refine these materials.
They may now be used as a reference for a beginner wishing to start using the EMB3Rs platform.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
To read full deliverable, please click on image to the left.
Graphics
A1 Poster (in English, Portuguese and Greek)



Banner (in English, Portuguese and Greek)


Public deliverables
D3.3 – Core Functionalities, Knowledge Base and Geographic Information System (GIS) Module
This deliverable presents the User and System Manuals for the Core Functionalities (CF) module, the Knowledge Base and the Geographic Information System (GIS) module.
The user manual for these modules will guide and help the user understand and navigate in these modules, as part of the integrated platform. The user manual is developed for an average user, and includes examples and infographics to promote the user-friendliness of the platform.
The system manual is designed for the advanced user. It is more comprehensive and includes the full variables description, along with the coding specifications and detailed presentation of all functionalities.
The EMB3RS project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 847121. This module is part of a larger assessment toolbox called the ‘EMB3RS platform’.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D3.4 – The EMB3Rs Techno-Economic Optimization Module
This deliverable presents the Techno-Economic Optimisation (TEO) module and includes the User and System Manuals.
The user manual for these modules will guide and help the user understand and navigate the module, as part of the integrated platform. The user manual is developed for an average user and includes examples and infographics to promote the user-friendliness of the platform.
The system manual is designed for the advanced user. It is more comprehensive and includes the description of all the inputs and the variables, along with the coding specifications and a detailed presentation of all functionalities.
It describes the functioning and use of the module. The EMB3RS project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 847121. This module is part of a larger assessment toolbox called the ‘EMB3RS platform’.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D3.5 – Market Module
This deliverable reports the findings of work performed under WP3 on tasks 3.1 and 3.3 related to the development and implementation of the Market Module (MM) and its integration into the EMB3Rs platform. In this deliverable, there are two manuals (the User and System Manuals) that will assist the platform’s users to explore the MM in the EMB3Rs platform.
Chapter 1 provides a brief introduction and the aim of the MM in the EMB3Rs platform, highlighting the main characteristics of the MM. The development of both short-term and long-term market analyses, including conventional and innovative market designs are addressed.
The System Manual (in chapter 2) provides all the theoretical background for the implementation and adaptation of the MM in the EMB3Rs platform. More precisely, the System Manual includes the complete description of the three different market designs implemented in the EMB3Rs platform, namely, (i) the Pool, (ii) Peer-to-Peer (P2P) and (iii) Community-based market. All the mathematical formulations used to model the market problem are provided. In addition, it includes a short description of the market analysis possibilities, namely, the short-term and long-term market analysis.
The User Manual (in chapter 3) provides a practical and succinct guide to the MM, allowing users to learn how to set up a market simulation case. This includes step-by-step details of inputs, simulation options and outputs for both short-term and long-term market simulation analysis. In addition, and for both short-term and long-term market simulation analysis, a test case is provided for the user to test the functionalities of the MM.
Chapter 4 describes the module report for both short-term and long-term analysis, as well as the simulation summary report for the EMB3Rs platform. The MM report comprises all the detailed outputs from the MM concerning the short-term and long-term market analysis, while the summary simulation report considers a brief overview of the MM results. Note that the summary simulation report are the results addressed in the overall platform report for the user, and therefore, an overview of each module’s results is considered.
Chapter 5 depicts the timeline of the developments of the MM, while Chapter 6 gathers the main conclusions.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D3.6 – Business Module
This report provides a comprehensive description of the Business Module developed under the EMB3Rs platform. The Business Module evaluates the financial viability of the excess heat or cold extraction and utilization project by introducing a private business perspective and a socio-economic one. The work on developing and deploying the Business Module is part of work package 3. This document is divided into two manuals: 1) System manual and 2) User manual. The system manual provides the theoretical description of the business module to understand the underlying theoretical framework and to reproduce its functionality. The system manual also provides an overview of the integration of the business module with other modules developed under the EMB3Rs platform. On the other hand, the user manual focuses on the users of this module and explains in detail the technical requirements of the inputs and outputs to run the module.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D3.7 – EMB3Rs Unified Modelling Platform Final Demonstrator
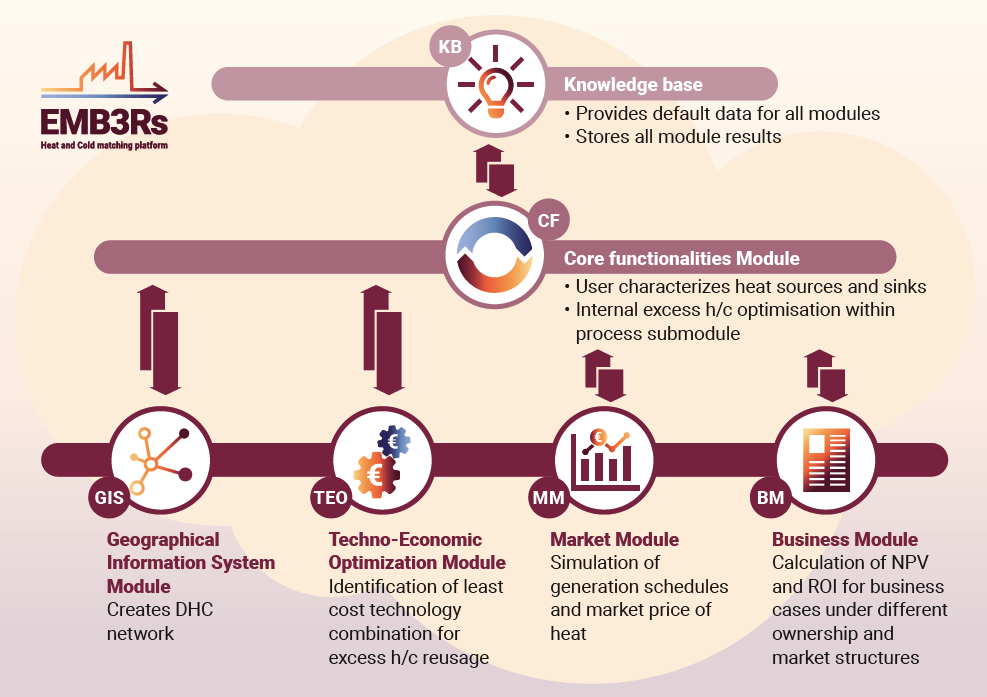
The EMB3Rs Unified Modelling Platform is a tool to assist on modelling the recovery of industrial excess heat and cold and its reuse to meet final energy demand within and beyond the boundaries of industrial sites. The tool consists on several simulation modules, a knowledge base where all data is stored and a core functionalities module where all interaction between user, knowledge base and analysis modules is handled.
EMB3Rs fully replaces the current, mostly manual, analysis process, typically hired to external entities (consultants) with specific expertise in the different analysis dimensions. It was conceived to be user-friendly and intuitive in such a way that even non expert users are able to find possible scenarios to recover industrial excess heat and cold.
This document describes the operation of the platform, from the user account creation, infrastructure creation, configuring a simulation, how the different modules are involved and the output reports to the user. Some of this information is closely related to the deliverables describing the platform, such as D3.1-D3.6.
This document starts with an EMB3Rs overview, then presents the platform and its basic features; it proceeds with a brief description frontend and how users shall interact with the platform; the following sections describe how a simulation will be configured and run by a user and how will the results be presented in the reports; the last section presents an overview of the backoffice where administrators of the instance may configure the inner functionalities of the platform.
This Document describes the EMB3Rs Platform and how to use it, and refers to the User Manual. It starts with sections for a typical final user, such as account creation, interaction with the map, adding infrastructures to the platform, configuring a simulation, an overview of the simulation reports and an introduction to the challenges participation.
The second part of this document covers the administration features and is mainly aimed to the platform administrations. It covers the installation and deployment of and EMB3Rs instance and the details of the backoffice, such as the user and roles management, template definitions and simulation and challenges definitions.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D5.1 – WP5 Final Report
Work Package 5 – Platform Scalability and Deployment used a combination of the
insights from WP4 Sector-Specific Platform Demonstration, desktop research,
lessons learned from previous work in the RHC (residual heat and cold) domain and
interviews with experts and practitioners to address the following tasks:
T 5.1 Scalability and Replicability of Proposed Solutions
T 5.2 Industry Wide Solutions and Multi-Sectorial Applications
T 5.3 Path to Finance and Wide-Scale Deployment of Waste Heat/Cold Recovery
Task 5.1 first analyses the replicability of the solutions by comparing the context and
scope of the problems solved in the seven Case Studies to those of the overall, reallife
industrial environment that the EMB3Rs platform can be expected to tackle. Next,
the potential to scale the platform is assessed based on two main factors – limits to
its functionality and data requirements.
The assessment of the replicability of solutions was carried out in a systematic way
for each parameter defining the scope of solutions, sources, sinks and grid that was
identified as relevant for the replicability. An overview of the findings is provided in
Table 1 below. It shows that to a large extent, the platform has covered in the Case
Studies the relevant range of the problems that it can be expected to encounter when
applied to real-life problems outside of the project, and be expected to replicate valid
solutions. The one exception to this is the number of sinks, where the range covered
by the platform were two orders of magnitude lower than the biggest district heating
networks in existence currently. However, the platform is not intended to model
problems of this scale, as this is the domain of dedicated teams of RHC experts with
professional, commercial tools. For all other central parameters of the RHC use, the
solutions provided by the platform demonstrate that it can cover the entire range of
potential problems which it will be applied to.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
D6.2 Project Website and Social Media Channels
The present deliverable is “Other” in nature, i.e. it is not a report. For convenience, we provide a short report about the structure and the features of the EMB3Rs website and the EMB3Rs social media channels on LinkedIn, Twitter, ResearchGate and YouTube.
The EMB3Rs website is set up along the details of Task 6.2 described in the Work Plan Table of Annex 1 “Innovation Action” of the Grant Agreement and the rules governing in the Consortium Agreement signed by the partners.
D6.3 Dissemination Kit: Poster, Banner and Brochure
Dissemination and awareness activities are a core part of the EMB3Rs project and will ensure that the tools and results developed within the project are communicated and exploited by relevant target audiences.
In order to reach this objective, i.e. to promote the project to both stakeholders, policy makers, potential investors and the public, a number of different dissemination and communication tools are required.
As outlined in D6.1, a dissemination kit – including brochure, A1 poster and roll-up poster – is part of the communication strategy. The brochures are for wide, individual distribution to potential end‐users and other stakeholders, the posters support the communication of EMB3Rs project at fairs and conferences.
The dissemination kit was originally scheduled for M6 (see D6.1). As a new partner joined in M6, its approval of the print material had to be awaited. Thus the scheduled date of D6.3 was updated to M8 in the project‘s amendment request.
D6.9 Best Practices in Communication and Dissemination Booklet
The Best practices in Communication and Dissemination Booklet describes the most successful communication tools used in EMB3Rs project.
D6.10 Open digital research data
Collection of research data (dully anonymized and in compliance with data protection
and confidentiality obligations) generated during the project has been deposited at
Zenodo’s open data repository (with DOI 10.5281/zenodo.7994255), to allow for the
verification and replicability of the calculations performed. This has been done
considering the FAIR principles, and promotes the transparency and accessibility of
the research data generated during the EMB3Rs project duration.
This report may be subject to further updates upon revision of the European Commission, and their final version will be made available when approval is granted.
Scientific Publications
Decarbonisation Pathways for District Heating Sector: A Policy and Private Business Perspective
M. Bilal Siddique, P. Sieverts Nielsen, D. Keles
DISTRICT HEATING refers to a central supply of heat to fulfil the space heating and hot water demand of buildings. District heating network comprises of central production units along with distribution network and occasionally, a transmission network for larger district heating networks. District heating offers many local environmental and economic benefits like reduced air pollution by eliminating individual heating at houses, utilising local energy
resources, flexibility in choice of heat production technology, creating more jobs, and eliminating energy poverty[1].
At a national level, high penetration of district heating makes the whole energy system more efficient and increases the share of renewable energy, as evident from the experiences of Denmark and Sweden [2], [3]. While the penetration of district heating is very high in Nordic countries of Denmark, Sweden, and Finland, a substantial potential of district heating expansion exists in other European countries where about 50% of heat demand at the European level can be supplied by district heating to achieve decarbonisation that is affordable [4].
The district heating sector faces the challenge of decarbonisation just like the whole energy sector. Furthermore, the reduced heating demand resulting due to temperature increase and investment in energy renovations of buildings due to ambition policy push [5] threaten the profitability of existing district heating companies in the future.
In this study, a comprehensive assessment of the future development of the district heating sector is conducted from the perspective of a whole energy system. This study tackles the challenges concerning future optimal fuels and technology shifts to achieve decarbonisation in future when heat demand is expected to reduce. The implications of future development in the district heating sector on policymakers and district heating companies are discussed.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Residential district heating network with peer-to-peer market structure: The case of Nordhavn district
A. S. Faria, T. Soares, L. Frölke
Over the last decades, district heating has been under development, especially the technologies like heat pumps, solar thermal and cogeneration. However, there is still a long way to go regarding regulation, legislation and market liberalization, which varies across countries and regions. The objective of this work is to investigate the potential benefits of decentralized district heating systems in residential areas. By studying a case study of EnergyLab Nordhavn, a residential area in Copenhagen, Denmark, the paper compares the market out-comes of decentralized systems such as community markets to the centralized pool market currently in practice, under the EMB3Rs platform. The study focuses on key market outputs such as dispatched production, revenues, and daily consumption patterns. Additionally, the paper examines the impact of advanced features such as flexible heat consumption and network awareness in the market. The results of this research suggest that decentralized district heating systems have the potential to improve market outcomes and increase energy efficiency in residential areas.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Impacts of earlier natural gas phase-out & heat-saving policies on district heating and the energy system
M. B. Siddique, P. S. Nielsen, M. B. Rosendal, I. G. Jensen, D. Keles
Decarbonizing the district heating sector is essential for an affordable energy transition. Decarbonization strategies focusing on the interaction between power sector, individual heating technologies, heat-saving measures, and district heating expansion are missing in literature. We use energy system investment optimization to analyse the impact of decarbonization policies on district heating by comprehensively modelling the above-mentioned interaction across power and heating sector, and within the heating sector. We model decarbonization policy scenarios of massive investment into heat-saving measures and an earlier natural gas phase-out by 2030. Using Denmark as a case study, we identify policy-driven investments into heat-saving measures as non-optimal. Our results indicate that district heating expansion facilitates an earlier natural gas phase-out, which is a viable policy that inflicts only 0.07% extra system cost compared to a scenario with only net-zero emission targets. Furthermore, we find that decarbonized district heating sector has a very high reliance on industrial excess heat, biofuels, and electrification. A biomass tax reduces the high utilization of raw biomass and promotes its more sustainable use in carbon capture and storage. Our results show a cogeneration capacity reduction, which poses a challenge to the business model of conventional Danish district heating companies.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Market integration analysis of heat recovery under the EMB3Rs platform: An industrial park case in Greece
A. S. Faria, T. Soares, G. Goumas, A. Botzios, J. M. Cunha, M. Silva
District heating is a system for distributing heat from a central source, such as a boiler plant or a combined heat and power plant, to multiple industries, buildings or homes within a defined geographic area. This system can use different energy sources, including fossil fuels, biomass, solar thermal, and geothermal energy, to provide customers with heating, hot water, and other services. In light of these benefits, this work aims to present a thorough study of a Greek industrial park case. The work is supported by the EMB3Rs platform that allows performing a feasibility analysis of the system. In particular, this work explores the market module of this platform to provide a detailed market analysis of energy exchange within the Greek industrial park. The results pinpoint the effectiveness of the platform in simulating different market designs, centralized and decentralized market designs, making it clear the potential benefit
the sources in the test case may achieve by engaging in a market environment. Different options for market clearing are considered in the study, for instance, including CO2 signals to reach carbon neutrality or community preferences to increase community autonomy. One can conclude that excess heat from existing sources is enough to cover other industries/facilities’ heat demand, leading to environmental benefits as well as a fairer financial profits allocation.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
The role of district heating in the future European energy system
F. Gaballo, P. S. Nielsen, B. S. Khan, A. Heller
District heating (DH) is often regarded as a sustainable supply of heat – improving energy efficiency and contributing to net zero emission targets. We analyse the expansion potential of DH in several EU Countries from the perspective of the whole energy system, which comprises interconnected heat power and transport sectors under different scenarios of heat demand development. Our results show a strong potential for DH expansion in most of the countries analysed with an overall share of DH increased from 8% to 40%. Among the countries analysed, Germany, Netherlands, UK, France, and Norway showed the most potential as presently, the DH in these Countries is almost non-existent. The role of potential exploitation of waste heat from electrolysers is also evaluated, and the results show a promising expansion with more than 50 TWh of excess heat introduced in the district heating grid with a 4% higher expansion of DH. We ultimately highlight the need for a comprehensive policy and market framework to promote expansion of energy efficient DH system and achieve an affordable decarbonization of the heating sector.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Techno-economic modelling and optimisation of excess heat and cold recovery for industries: A review
S. Kumar, J. Thakur, F. Gardumi
Recovery and use of industrial excess heat and cold are expected to play a huge role in the decarbonisation of heating and cooling systems in Europe. From the perspective of the industry, it could also promote a coupling between the sectors and help offset emissions, leading to a sustainable industry. However, there exists a gap in knowledge regarding the planning of infrastructure for utilization of excess heat, specifically for industries. This study aims at reviewing energy system optimisation tools that can be used by industrial stakeholders to plan energy investments for recovery and utilization of excess heat and cold. Through a study of existing energy systems models, seven tools are found suitable for analysing industrial excess heat and cold recovery. A detailed review of these tools is conducted and they are compared. The capability of the models to represent and analyse industrial excess heat and cold recovery options are critically discussed. The main requirements of such an analysis are used to establish criteria for comparison. The results of the comparison are used as a knowledge base to form a simple decision support tool to help industrial stakeholders choose the most suitable energy system model. The results from the review, comparison and decision support tool indicate that none of the models is capable of fulfilling all needs in every case. They also highlight that the choice of the tool depends especially on the required temporal and spatial resolution and its interoperability.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Evaluating Efficient Use of Waste Heat Energy and Decarbonisation Potentials Using the EMB3RS Platform: UK Energy-Intensive Industries
M. Kumar, F. Martin
This study innovatively intended to assess the quantity and quality of excess waste heat and explore the opportunities for efficient use of waste energy produced by casting and ceramic industries in the UK using the heat and cooling platform – EMB3RS.
The platform integrated techno–economic optimisation, GIS, market and business modules to provide insights for energy–intensive industries and discover ways of reusing their excess thermal energy
(ESCI and PDM 2021). This study proposes using this platform to answer questions on the cost–effective options and the optimal opportunity for decarbonisation and reuse of waste heat in these industries. For example, can the recovered quantity of heat waste be used internally for space heating, converted to electricity, or sold to a heat district network?
Further, what market design options is possible to enable energy trades between producers and consumers to gain economic and decarbonisation benefits?
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Market Integration of Excess Heat
L. Froelke, I. Palm, and J. Kazempour
Excess heat will be an important heat source in future carbon-neutral district heating systems. A barrier to excess heat integration is the lack of appropriate scheduling and pricing systems for these producers, which generally have small capacity and limited flexibility. In this work, we formulate and analyze two methods for scheduling and pricing excess heat producers: self-scheduling and market participation. In the former, a price signal is sent to excess heat producers, based on which they determine their optimal schedule. The latter approach allows excess heat producers to participate in a market clearing.
In a realistic case study of the Copenhagen district heating system, we investigate market outcomes for the two excess heat integration paradigms under increasing excess heat penetration.
An important conclusion is that in systems of high excess heat penetration, simple price signal methods will not suffice, and more sophisticated price signals or coordinated dispatch become a necessity.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
On the efficiency of energy markets with non-merchant storage
L. Froelke, E. Prat, P. Pinson, R. Lusby, J. Kazempour
Energy market designs with non-merchant storage have been proposed in recent years, with the aim of achieving optimal integration of storage. In order to handle the timelinking constraints that are introduced in such markets, existing works commonly make simplifying assumptions about the end-of-horizon storage level. This work analyzes market properties under such assumptions, as well as in their absence. We find that, although they ensure cost recovery for all market participants, these assumptions generally lead to market inefficiencies. Therefore we consider the design of markets with non-merchant storage without such simplifying assumptions. Using an illustrative example, as well as detailed proofs, we provide conditions under which market prices in subsequent market horizons fail to reflect the value of stored energy. We show that this problem is essential to address in order to preserve market efficiency and cost recovery. Finally, we propose a method for restoring these
market properties in a perfect-foresight setting.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Excess heat regulations, contracts and business models– with a special focus on excess heat opportunities in Denmark
P. Sieverts Nielsen, B. Siddique Khan, D. Møller Sneum
The production of waste heat – or excess heat is substantial in the European Union. Despite the potential for excess heat utilisation several barriers exist. This paper identifies different barriers and enablers for excess heat utilisation, which is based on an analysis carried out in four European countries as part of EU funded project. The detailed literature review on the status of excess heat recovery identified a very diverse nature of district heating regulations in the different countries along with different layouts of contracts and business models. An analysis of the potential for excess heat utilisation in Denmark shows a substantial increase in excess heat utilisation in district heating. The identified barriers include access to a market (district heating network), lack of a comprehensive regulatory framework along with standardising contracts, lacking sinks (end users), and absent financial incentives to make excess heat a viable option for the potentially involved stakeholders.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Techno-economic optimization of the industrial excess heat recovery for an industrial
S. Kumar, J. Thakur, A. Kök, J. M. Cunha, F. Gardumi
This paper assesses the decarbonisation potential of utilizing industrial excess heat to meet the baseload heating requirements of a district heating network (DHN) located in the Portuguese capital. It performs an economical comparison between two integration procedures: (i) extending the pipeline to the excess heat source; and (ii) using a continuous string of portable thermal storage modules.
In this scope, this work assesses the integration of the excess heat from a municipal waste-to-energy plant located 5km from a district heating and cooling network and the decarbonisation potential achieved by meeting the baseload heating requirements of the DHN. For the characterization of excess heat and economic analysis, the EMB3RS platform was used. The analysis showed that laying out a new pipe route was more economically feasible (with a levelized cost of heat of 17,25€/MWh), meeting the baseload consumption with a decarbonisation reduction potential of 30%. The higher levelized cost of heat (LCOH) of the portable thermal storage solution is mainly due to the high daily replacement cost for the thermal stores.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Decarbonization potential of integrating industrial excess heat in a district heating network: The Portuguese case
J. M. Cunha, Z. Mourão, A. S. Faria, T. Soares, J. Nereu
This paper assesses the decarbonisation potential of utilizing industrial excess heat to meet the baseload heating requirements of a district heating network (DHN) located in the Portuguese capital. It performs an economical comparison between two integration procedures: (i) extending the pipeline to the excess heat source; and (ii) using a continuous string of portable thermal storage modules.
In this scope, this work assesses the integration of the excess heat from a municipal waste-to-energy plant located 5km from a district heating and cooling network and the decarbonisation potential achieved by meeting the baseload heating requirements of the DHN. For the characterization of excess heat and economic analysis, the EMB3RS platform was used. The analysis showed that laying out a new pipe route was more economically feasible (with a levelized cost of heat of 17,25€/MWh), meeting the baseload consumption with a decarbonisation reduction potential of 30%. The higher levelized cost of heat (LCOH) of the portable thermal storage solution is mainly due to the high daily replacement cost for the thermal stores.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Mutual-benefit of district heating market and network operation for prosumers integration
A. S. Faria, T. Soares, J. M. Cunha, Z. Mourão
The integration of prosumers (consumers who can both consume and produce energy) in a current district heating network (DHN) brings new challenges to the market and DHN operation, since they can change the thermal flow in the DHN and increase competition in the district heating market.
In this scope, this work proposes the implementation of a coordination methodology based on a peer-to-peer (P2P) market to enable bilateral energy trades between producers, prosumers and consumers, coupled with the DHN operation.
A Nordic DHN containing prosumers is used to test and validate the proposed methodology. The results point out that the coordination methodology is able to provide compromise solutions between the market negotiation and the DHN operation. An important conclusion is that the coordination methodology encourages prosumer integration in DHN, increasing market competition that may pull down the energy costs for consumers while avoiding DHN’s operating and management burdens.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
A network-aware market mechanism for decentralized district heating systems
L. Frölke, T. Sousa, P. Pinson
District heating systems become more distributed with the integration of prosumers, including excess heat producers and active consumers. This calls for suitable heat market mechanisms that optimally integrate these actors, while minimizing and allocating operational costs. We argue for the inclusion of network constraints to ensure network feasibility and incentivize loss reductions. We propose a network-aware heat market as a Quadratic Program (QP), which determines the optimal dispatch and a set of nodal marginal prices. While heat network dynamics are generally represented by non-convex constraints, we convexify this formulation by fixing temperature variables and neglecting pumping power. The resulting variable flow heating network model leaves the sign and size of the nodal heat injections flexible, which is important for the integration of prosumers. The market is based on peer-to-peer trades to which we add explicit loss terms. This allows us to trace network losses back to the producer and consumer of these losses. Through a dual analysis we reveal loss components of nodal prices, as well as relations between nodal prices and between seller and buyer prices. A case study illustrates the advantages of the network-aware market by comparison to our proposed loss-agnostic benchmark. We show that the network-aware market mechanism effectively promotes local heat consumption and thereby reduces losses and total cost. We conclude that the proposed loss-aware market mechanism can help reduce operating costs in district heating networks while integrating prosumers.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Exploring the role of households’ hurdle rates and demand elasticities in meeting Danish energy-savings target
K. S. Andersen, C. Wiese, S. Petrovic, R. McKenna
The EU’s Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) sets a binding target for energy-savings in EU member states. The EED further requires member states to perform ex-ante evaluations of energy efficiency policies implemented to achieve these savings. However, ex-ante evaluation of energy efficiency policies is difficult as it requires detailed modelling of end-users’ investment and energy demand behaviour. This paper details the Danish IntERACT modelling approach for ex-ante evaluation of energy efficiency policies directed at residential heating. IntERACT integrates the energy system model TIMES-DK into a computable general equilibrium framework. The paper explores the potential for meeting Denmark’s EED-target through a policy-induced increase in households’ investments in energy efficiency retrofits. The paper considers the effect of energy efficiency policies on households’ investment behaviour by applying different levels of hurdle rates on households’ investments in energy efficiency retrofits. The paper shows that reducing the hurdle rate from 25% to 4% could meet more than a third of Danish energy-saving requirements for the period 2021–2030. This result includes a direct rebound effect of 31%. Finally, the paper demonstrates that reducing the hurdle below 10% has a substantial negative impact on households’ disposable income, making such policy less viable from a policy perspective.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.
Liberalized market designs for district heatingnetworks under the EMB3Rs platform
A. Faria, T. Soares, J. M. Cunha, Z. Mourão
Current developments in heat pumps, supported by innovative business models, are driving several industry sectors to take a proactive role in future district heating and cooling networks in cities. For instance, supermarkets and data centers have been assessing the reuse of waste heat as an extra source for the district heating network, which would offset the additional investment in heat pumps. This innovative business model requires complete deregulation of the district heating market to allow industrial heat producers to provide waste heat as an additional source in the district heating network.
This work proposes the application of innovative market designs for district heating networks, inspired by new practices seen in the electricity sector. More precisely, pool and Peer-to-Peer (P2P) market designs are addressed, comparing centralized and decentralized market proposals. An illustrative case of a Nordic district heating network is used to assess the performance of each market design, as well as the potential revenue that different heat producers can obtain by participating in the market. An important conclusion of this work is that the proposed market designs are in line with the new trends, encouraging the inclusion of new excess heat recovery players in district heating networks.
To read full paper, please click on image to the left.